Time Dilation Effect
Einstein’s Theory of Special Relativity defines the behaviour of physical quantities moving at very high speeds relative to each other. This has major implication for our experience of time, distance, mass and for physical quantities derived from these.
The behaviour of time is defined by the following formula. A time interval within a particular frame or system is denoted by ∆t0.
Another observer moving at a speed (velocity) v relative to this system will experience this time interval as ∆t‘. This is altered from ∆t0 by the factor √(1 – v2/c2), as defined in the formula:
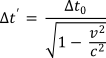
where c is the speed of light (close to 300,000km / second).
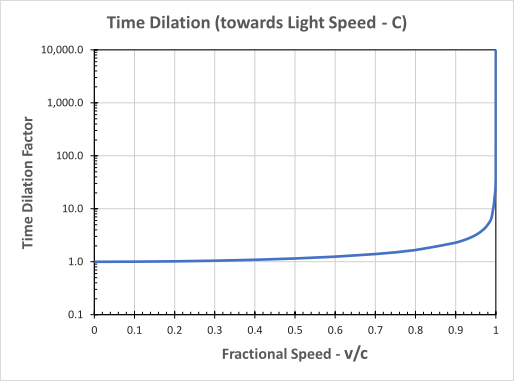
We can illustrate this relationship pictorially in the attached graph above. The horizontal direction or axis indicates speed as a fraction of the speed of light. The vertical axis shows time for the external observer relative to within the system. This graph demonstrates that, as we move relative to a particular system, we perceive time within that system expanding or dilating.
Ultimately it dilates to infinity at the speed of light. For modest speeds, typical of earth, the dilation effect is negligible. Close to light speed the effect is very pronounced.
We can take earth as a reference system, for example. This means that time on earth dilates to infinity, for any observer moving at light speed relative to earth. Infinitely dilated time is the very definition of Eternality! This process connects earth time to the Eternal.
Alternatively, we can view this process as a contraction from Eternality into finite time. It is a localisation and projection into discrete intervals of time, such as we normally experience on earth.
Length Contraction
We have a comparable process in play for distance or length. Distance effectively is a measure of separation.
The behaviour of length is defined by the following formula. A length or separation measure within a particular frame or system is denoted by L0.
Another observer moving at a speed v relative to this system will experience this length as L’. This is altered from L0 by the factor √(1 – v2/c2), as defined in the formula:
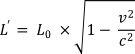
where c is the speed of light.
We can similarly illustrate this relationship pictorially, as in the second graph.
The arrangement of the graph is mostly similar to before. Note that the vertical axis is logarithmic, with 1.0 at the top and zero towards infinity at the bottom. This helps illustrate the shape of the curve at very small scales.
This graph demonstrates that, as we move relative to a particular system, we perceive length within that system contracting. Ultimately it contracts to zero at the speed of light.
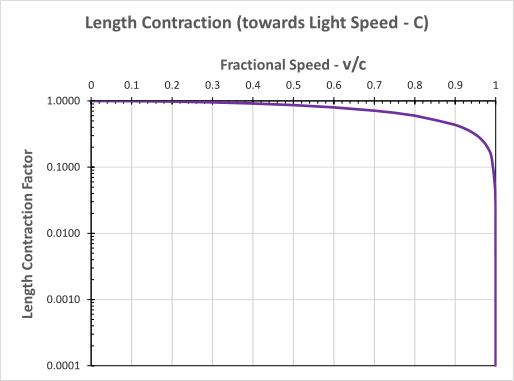
For modest speeds, typical of earth, the contraction effect is negligible. Close to light speed the effect is very pronounced.
Again, we can take earth as a reference system, for example. This means that lengths or distances on earth contract to zero, for any observer moving at light speed relative to earth. This effectively means that there is no separation, at the level of that observer. Lack of separation is also the very definition of Wholeness or Transcendence! This process also connects earth to the higher levels in creation. Looking at it the other way round, from the level of Wholeness we have a projection into separation and localisation, at the level of earth.
Nature of Light
Light and light speed are critical in these relationships. If we look at the structure of the relationship factor in the formulae above, √(1 – v2/c2), we see that it forms a 90⁰ triangle, as illustrated in the attached diagram. Here the speed v is shown horizontally, with the red arrow at the bottom. The speed of light c corresponds to the long side (hypotenuse) of the triangle. Then the relationship factor √(1 – v2/c2) arises in the vertical side, associated with the green arrow.
For most practical cases in the material world (where there is mass) the speed is several orders of magnitude smaller than the speed of light C. So the triangle has c very close to 90⁰ to and the relationship factor is virtually 1.
V represents any material speed in any direction within the 3D material world. So the speed of light is essentially perpendicular to such material speeds . This 90⁰ angle provides independence between the quantities.
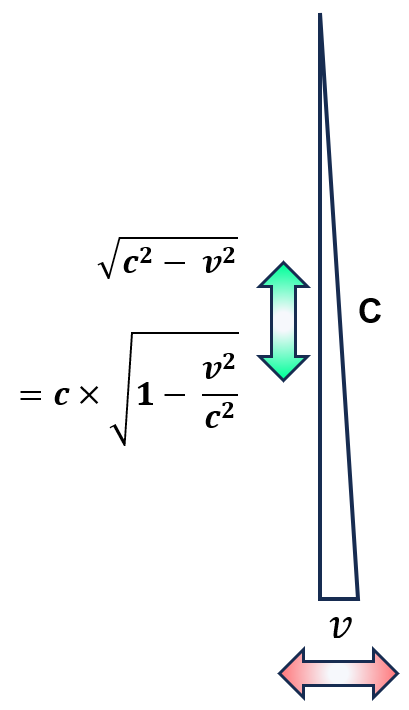
For example, movement in one direction does not generate any movement at 90⁰ to this direction. This is why independent dimensions, for example in 3D, are at 90⁰ (orthogonal) to each other. So the speed of light is essentially independent of simple material speeds.
This aligns with the Principle of Relativity or Einstein’s first postulate. This states that – the laws of physics are the same in every inertial reference frame. We need to qualify in the above that the material speeds in question relate to inertial systems. These are simple systems that are not under the net influence of forces. Hence the name Special Relativity. More complex systems that are under the net influence of forces, such as gravity, are treated in Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity.
Einstein’s second postulate in Special Relativity states directly that – the speed of light (in vacuum) is the same in all inertial reference frames and is independent of the motion of the source.
In order for light to be independent of all dimensions in 3D materiality, in needs to be outside these dimensions. This suggests that the speed of light associates with higher dimensional levels in creation. It is crossing higher dimensional boundaries.
Matter & Energy
Relativity also associates matter and energy, with matter being a condensed and localised form of energy. The relationship between energy and matter is defined by the following formula:
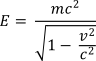
Here E is the total energy and m is the mass of a particle or body of matter.
The total energy E varies, depending on the relationship between the matter speed v and the speed of light c. This variation is similar to the time dilation effect mentioned above. The behaviour is illustrated in the first graph.
Material speed v is generally very much less that the speed of light c. The relationship factor in the formula above is then very close to 1 and we get Einstein’s famous formula:
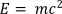
This is the energy inherent or condensed in the mass m. This is referred to as the rest mass and its associated rest energy.
For larger matter speeds approaching the speed of light, the energy increases dramatically, as illustrated in the first graph. This energy has to be provided to the particle or body, to accelerate it to such high speeds. At the speed of light the energy associated with a mass becomes infinite. So, it would take an infinite amount of energy to accelerate any mass greater than zero to light speed. This means that it is effectively impossible for material bodies with definite mass to reach light speeds.
Particles that do reach light speeds have zero rest mass. Zero mass particles always travel at light speed. Examples of such particles include the photon, the quantum of light energy.
This behaviour establishes a definite boundary between energy manifesting as light (electro-magnetic radiation) and energy condensed into matter forms. The infinitely expanded time and non-separated states indicated for light speeds above are not practically achievable for matter forms. Matter effectively entails a projection into localised time and finite forms, related to its density.
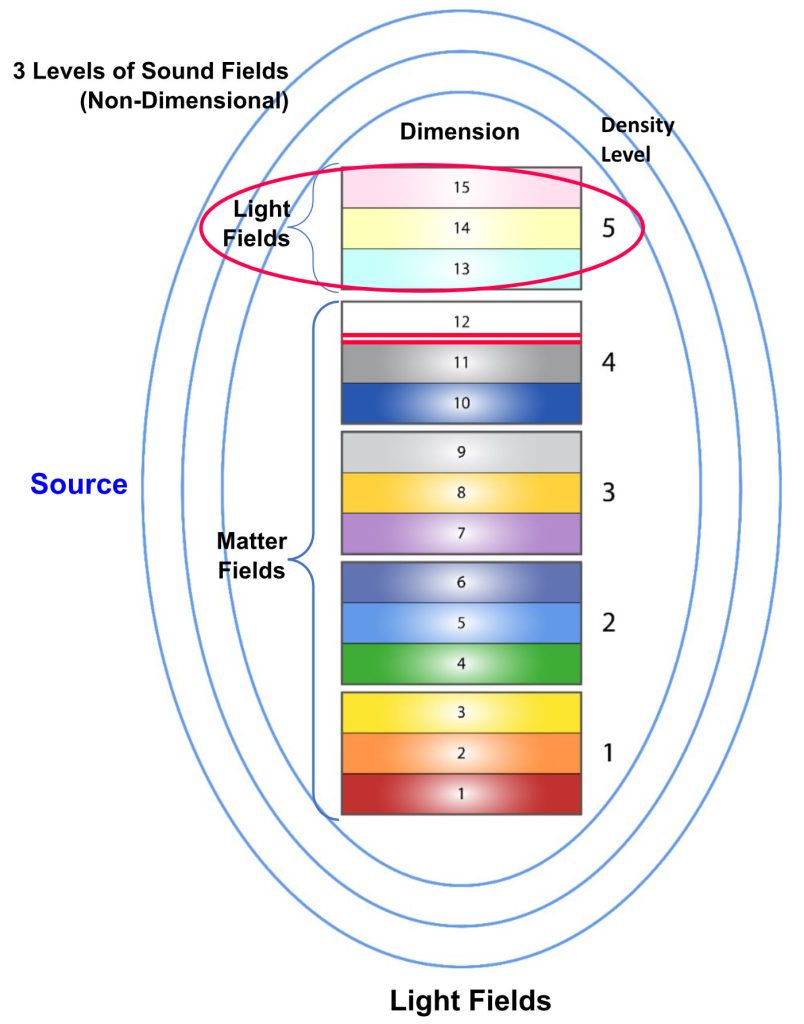
This stratification in creation is illustrated in the dimensional structure diagram discussed earlier and replicated here. In this the Light Fields are indicated as Density Level 5. These are above the Matter Fields and are associated with a purer more open form of energy that isn’t limited by materialisation. Below this level we have increasingly dense levels of the Matter Fields. Above the Light Fields we have progressively purer and more integrated forms of Consciousness, ultimately united in the wholeness, freedom and infinite Life of Source.
Creation is holographic, where the whole is present to every part, while all is contained within the whole. So, the higher realities in creation pervade all levels in creation. Consciousness, as the over-arching reality, is present to all levels and can move between levels, with varying degrees of freedom.
It is present, as the life that animates all that lives in creation, including here on our 3D planet earth. Likewise, light and its characteristic behaviour are present in our world and everyday lives.
Significance of Speed of Light – C
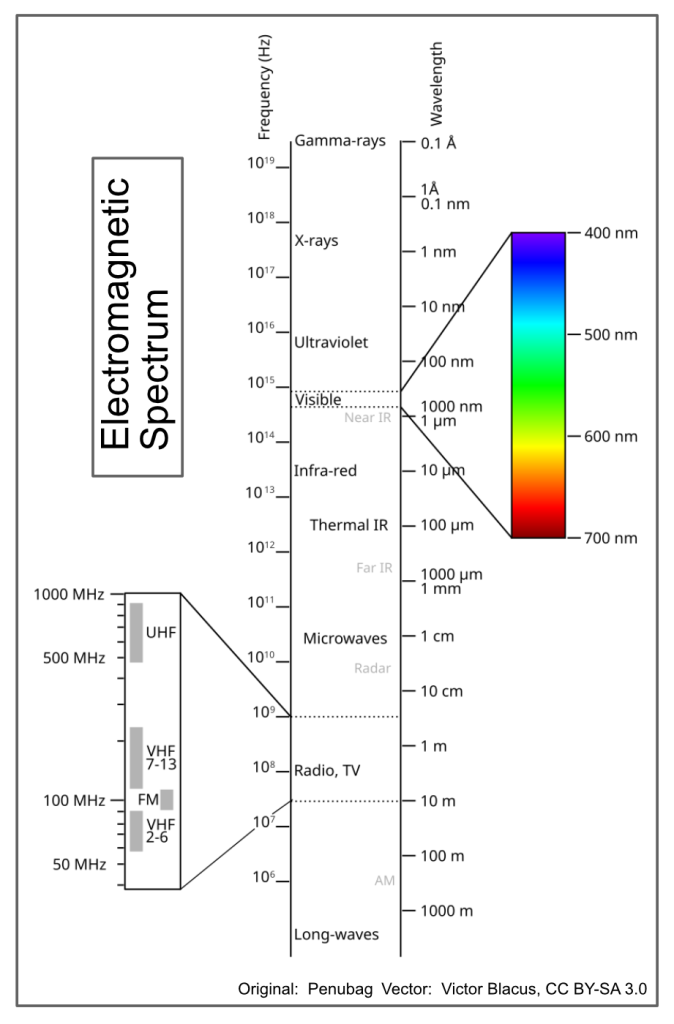
Physical light is an electro-magnetic phenomenon. It propagates as waves of electro-magnetic energy oscillating in a particular frequency range. The extended range of electro-magnetic frequencies is illustrated as the Electromagnetic Spectrum in the diagram attached. Lower frequencies correspond to radio waves, higher frequencies to microwaves and still higher to light. Frequencies higher than light correspond to X-rays, cosmic rays and so on. Within the band of light frequencies different colours derive from different frequencies.
All these electro-magnetic waves, including light, travel at a speed determined by the electrical and magnetic properties of space, or whatever medium they are travelling through. This is referred to as the speed of light. It is denoted by the symbol ‘C’.
This relationship is defined by the formula:
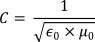
Here εo is the Greek letter (e) representing the electrical nature (elasticity) of space. μ o is the corresponding Greek letter (m) representing the magnetic inertia. These two quantities define the speed of light.
Space and time are not as absolute, rigid nor static as we might believe them to be. They can expand, contract, flow and be shaped. We usually experience space in terms of separation. But separation can have both space and time elements. For example, the separation between a plane taking off from New York and landing in San Francisco comprises the physical separation between these two cities and the time difference between the events. We normally think of space and time as separate. But physics indicates that they are closely coupled in the larger scheme of things.
Separation is determined by both distance and time in the following relationship:
Separation (S2) = C2 x Time (T2) – Distance (D2).
Here C is the speed of light, as indicated above.
Now from a Source perspective there is no separation. Source integrates all reality.
So, S in the relationship above is zero at this level. Rearranging the relationship accordingly we get:
D2 = C2 x T2 or
C = D(istance) / T(ime)
From a Source perspective then ‘C’ measures the expansion of Distance through Time. It measures the flow of space through time.
The speed of light measures the rate of formation or projection of space.
Combining 1 /√(∊0 x μ0) = C = D / T, we see that fundamental electrical and magnetic properties influence the structure of space and time. They determine the speed of light, which in turn determines the rate of formation of space. Thus, different dimensional levels can have differing electrical & magnetic properties that alter the nature of space and time and influence the corresponding experience of life within their realms.
Creation Projection
We have seen earlier how time intervals on earth, for example, dilate to infinity as seen by an observer travelling at the speed of light relative to earth. Likewise, length intervals or separation distances contract to zero for such an observer. Now the speed between the observer and earth is relative. Any observer, experiencing such transcendence of time and zero separation is approaching Source conditions.
Source is the absolute reality. It doesn’t need to go anywhere, because it is everywhere. It transcends location in both space and time. Travelling anywhere is meaningless. So, it is more meaningful to regard Source and near Source states as being at rest. This means that it is the artefacts within creation, such as earth, that are moving, in relation to Source.
Is it meaningful to speak of earth moving, at such as the speed of light, in relation to Source? Yes, it is. Projection into creation entails motion. This entails projection into separation and localisation in finite intervals of time. We have seen above that, coming from a state of no separation in wholeness, the speed of light defines the relationship between the rate of separation and the formation of time. The speed of light is at the very heart of the process of formation of the space and time, we experience on earth and in physical reality generally.
When talking about motion in relation to Source, we’re not dealing with conventional physical motion. We’re not talking about the orbital or spinning motion of the earth or motion in relation to the galaxy or fixed stars. We’re dealing with the formation of the foundations of physical reality, with the manifestation of space and time in this reality. Our experience of separation in space and finite cycles of time is a product of the creation process that projects this physical reality. The seeming paradoxes in the behaviour of space and time, as we approach light speeds, arise from our beginning to encounter fundamental creation processes.
In addition to projection into separation in space and finite time, we also have localisation in finite forms. We have progressive densification into matter. We have energy condensing into matter, waves projecting into particles, potentialities generating actualities and so on.
We have seen above that localised matter cannot move at light speeds in relation to any other such matter. This would require infinite amounts of energy. In order for localised matter to move at light speeds, it needs to reverse the processes that projected it into creation. It needs to de-localise, reduce density and move closer to its original energetic state. To ultimately reach light speeds, it must become massless. It must transcend matter and revert to its original light state.
Matter density and the localisation that goes with this is confined to the Matter Fields. It’s most localised and specific expression is in physical reality. This corresponds to Density 1, the most dense level of the four Density levels in the Matter Fields. Beyond this we are into the pure energy of the Light Fields in Density 5.
In dealing with light and associated speeds, we encounter some of the deeper ‘vertical’ processes that manifest creation. This is why light speed differs fundamentally from conventional physical speeds. We encounter processes of projection into density on the one hand and progressive integration and transcendence back to wholeness, with no separation and eternality, on the return cycle.
Matter is fundamental to our experience of individuality and separation in physical reality. As Einstein explained in his General Theory of Relativity, matter warps the space and time of its locality. This attracts other matter into this locality, generating what we experience as gravity. Gravity is key to keeping us grounded on a planet such as earth. Without this, the spinning of the planet would tend to hurl us into the vast isolation of space. Gravity helps to structure matter, for example in buildings, solar systems and so on.
Both matter and gravity interact with space and time. They are likewise affected by the processes associated with space and time.
The speed of light is determined by the electrical and magnetic properties of an environment. Electricity and magnetism form a fundamental polarity at the root of these creation processes. Higher level electricity and magnetism may be more subtle, powerful and conscious than its expression in physical reality. Electricity tends to be associated with elasticity and the flexibility of an environment to store energy. Magnetism, on the other hand, associates with inertia or resistance to motion. It stores energy to create motion. The two polarities interact to create oscillations.
Life and consciousness underly, animate and pervade all of these processes in creation. It transcends the Matter Fields and pure energy / Light fields, but is present to all of them. This is what provides meaning for and ultimately makes sense of everything.
